Multi-scale Group Decision-Making Employing Large Language Model for Sentiment-Oriented Grouping
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.61702/p4xkas36Keywords:
Group Decision-Making, Consensus reaching process, Grouping, multi-scale methodAbstract
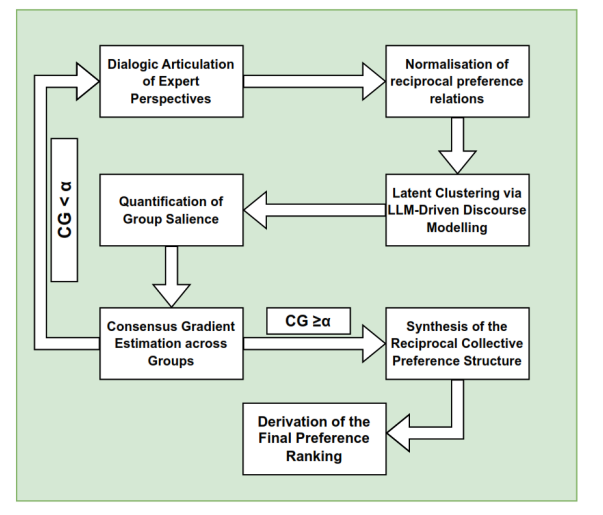
In contemporary decision-making scenarios involving multiple experts, the expression of opinions through natural language poses significant challenges for traditional analytical frameworks. As online collaboration expands, so does the heterogeneity of expert evaluations, both in scale and form, particularly when assessments are expressed via unstructured textual comments. Conventional Multi-scale Group Decision-Making methods, while effective in managing diverse evaluation metrics, often fall short in processing the semantic complexity of human language. This study proposes an enhanced Multi-scale Group Decision-Making framework that integrates a Large Language Model to classify experts' comments with greater contextual sensitivity. Unlike classical sentiment analysis methods, which rely on rigid lexical heuristics, Large Language Model captures deeper linguistic nuances, such as tone, intent, and implicit meaning, enabling a more precise grouping of experts based on their expressed attitudes. These refined groups contribute to a more coherent consensus process and lead to improved decision outcomes. The proposed approach advances group decision methodologies by bridging structured decision theory with state-of-the-art natural language understanding.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Cyber-Physical-Social Intelligence

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
CC Attribution 4.0






